Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are increasingly adopting technology to streamline operations and enhance security. One of the most transformative tools in modern business transactions is the digital signature. Digital signatures offer a secure, efficient, and legally binding way to sign documents electronically. As organizations move away from traditional paper-based methods, digital signatures provide significant benefits, improving both the security and efficiency of business transactions.
Definition
A digital signature is a technology that may be used for digital documents like Word, PDF, Excel, PowerPoint, and others. It is based on a mathematical algorithm of encoding and verification. Digital signature technology makes file authentication easier and confirms the sender’s identity as well as the content of the document. Additionally, the technology is employed to stop malware behaviours and safeguard vital organizational data.
Understanding Digital Signatures
An electronic version of a signature that may be used to verify the identity of the sender or signer of a document is called a digital signature. It guarantees that the document’s contents have not been changed while it is in transit and that the signer cannot retract their signature (non-repudiation). Digital signatures are based on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), where a pair of keys – one public and one private – are used to encrypt and decrypt data.
The private key, known only to the signer, is used to create the signature, while the public key is available to the recipient to verify the authenticity of the signature. Digital signatures are widely recognized as secure and legally valid across many industries and jurisdictions.
Security Advantages of Digital Signatures
Data Integrity:
Data integrity is guaranteed by digital signatures, which is one of their main security advantages. When a document is signed digitally, any attempt to alter its contents after signing will invalidate the signature. This is achieved through cryptographic algorithms that link the digital signature to the content of the document. As a result, businesses can be confident that documents have not been tampered with, ensuring trust in the accuracy of the information exchanged.
Authentication:
Digital signatures provide a robust way to verify the identity of the signer. Traditional handwritten signatures can easily be forged, while digital signatures are uniquely tied to the individual who created them. This authentication process is powered by digital certificates, issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). The digital certificate contains information about the signer and the CA, adding an additional layer of security by ensuring that the individual signing the document is who they claim to be.
Non-repudiation:
In business transactions, the concept of non-repudiation is critical. Non-repudiation means that the signer cannot deny having signed the document, as the digital signature is tied to both the individual’s identity and the document itself. This reduces the possibility of problems and offers legal protection. Digital signatures ensure that there is verifiable proof of signing, reducing the likelihood of fraudulent claims.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards:
Regarding the handling of electronic documents, many businesses are subject to strict regulatory regulations. Digital signatures help businesses comply with these regulations by providing secure and auditable records of transactions. For example, in sectors like finance, healthcare, and legal services, digital signatures are often required to meet standards such as the eIDAS Regulation in Europe, the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN Act) in the United States, and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Efficiency Gains through Digital Signatures
Streamlined Workflow:
One of the most significant advantages of digital signatures is the ability to streamline business processes. In a traditional setting, documents need to be printed, signed, scanned, and sent back to the relevant parties, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Digital signatures eliminate these steps by allowing documents to be signed and shared electronically. This leads to faster approval processes and reduces the need for physical document handling, especially in remote or global transactions.
Faster Turnaround Times:
With digital signatures, businesses can achieve much faster turnaround times for contracts, agreements, and approvals. Instead of waiting days or even weeks for a physical signature, documents can be signed and sent back within minutes. This increased speed helps organizations meet deadlines, close deals more quickly, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Cost Savings:
By eliminating the need for paper, printing, and postage, digital signatures lead to significant cost savings. Businesses no longer have to invest in physical document storage or pay for courier services to send important documents. Additionally, the reduced reliance on paper contributes to sustainability efforts, aligning with many companies’ goals to reduce their environmental impact.
Remote Accessibility:
In today’s increasingly remote and distributed work environment, digital signatures allow businesses to continue operating seamlessly, even when team members or clients are located in different parts of the world. Since documents can be signed electronically from any location with an internet connection, digital signatures facilitate smooth collaboration and communication. This is particularly valuable for organizations that rely on global partnerships or remote workforces.
Improved Document Management:
Digital signatures make it easier to organize and manage documents. Electronic documents signed with digital signatures can be stored and accessed in cloud-based systems, ensuring that records are available when needed. This simplifies document retrieval, reduces the risk of loss, and enhances overall operational efficiency. Furthermore, digitally signed documents can be easily tracked and audited, providing a clear record of who signed the document, when it was signed, and what changes (if any) were made.
Legal Validity of Digital Signatures
One of the main concerns businesses have when adopting new technology is its legal standing. Fortunately, digital signatures are legally recognized and enforceable in many countries around the world. Regulations such as the eIDAS Regulation in the European Union and the ESIGN Act in the United States have established clear frameworks for the use of digital signatures in both public and private sectors.
These laws ensure that digital signatures are legally binding, provided they meet certain criteria, such as the use of a digital certificate and compliance with relevant industry standards. This legal recognition gives businesses confidence that digital signatures can be used in contracts, agreements, and other legally significant documents without concern for validity.
Use Cases for Digital Signatures in Business Transactions
Contract Management:
Digital signatures are widely used in contract management, allowing businesses to expedite the signing of agreements with partners, clients, and employees. Whether it’s employment contracts, non-disclosure agreements, or sales contracts, digital signatures ensure a fast and secure process.
Financial Transactions:
In finance, digital signatures are used to sign loan agreements, investment documents, and other financial transactions. This ensures that sensitive financial information remains secure while speeding up the approval process for both businesses and customers.
Healthcare:
In healthcare, digital signatures are used to sign patient consent forms, prescriptions, and medical records. This helps healthcare providers comply with regulations like HIPAA while enhancing patient care through streamlined processes.
Government Services:
Many government agencies now use digital signatures to process forms, applications, and permits. This reduces bureaucracy and improves service delivery by enabling faster approval times for citizens and businesses alike.
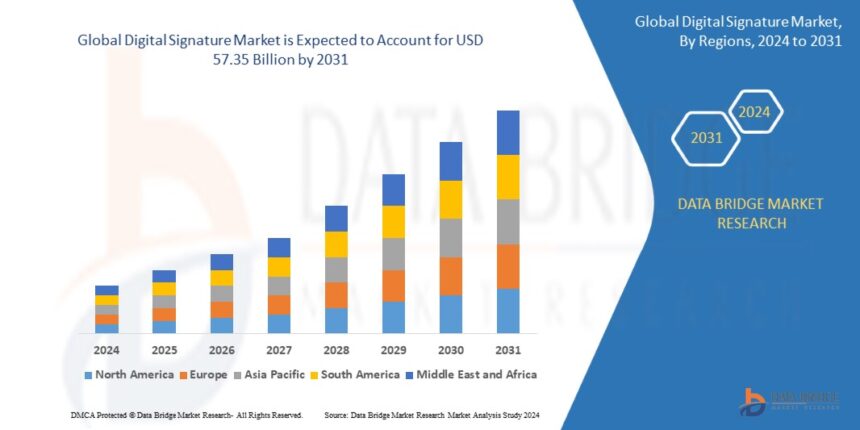
Growth Rate of Digital Signature Market
The size of the global market for digital signature was estimated at USD 6.15 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.19% from 2024 to 2031, to reach USD 57.35 billion.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-digital-signature-market
Conclusion
The adoption of digital signatures is transforming the way businesses conduct transactions, enhancing both security and efficiency. By providing a secure, legally recognized way to authenticate documents, digital signatures help prevent fraud, streamline processes, and reduce costs. In an increasingly digital world, businesses that embrace digital signatures are well-positioned to improve their operational efficiency, build trust with partners and clients, and stay ahead of regulatory requirements. As more industries recognize the benefits, digital signatures will continue to play a critical role in the future of business transactions.