Introduction
The workplace has experienced a dramatic upheaval in recent years. The rise of remote work, accelerated by global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic, has reshaped how businesses operate and how employees interact with their work environments. In this evolving scenario, Extended Reality (XR) technologies have emerged as powerful tools that bridge the gap between physical and virtual worlds, enhancing remote work and collaboration. XR encompasses Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), offering immersive experiences that can revolutionize remote work.
Definition
A variety of immersive technologies that smoothly combine real-world and virtual settings to create dynamic and captivating experiences are collectively referred to as extended reality (XR). Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) applications are examples of XR products and services. Using headsets or glasses, virtual reality (VR) immerses users in a totally digital environment to create an experience that mimics being physically present in a virtual world.
Understanding Extended Reality
Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR), and Virtual Reality (VR) are all included under the general term Extended Reality (XR). Each of these technologies offers unique capabilities that can transform remote work and collaboration:
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR immerses users in a fully digital environment, often using headsets like the Oculus Rift or HTC Vive. In a VR environment, users can interact with 3D objects and navigate virtual spaces as if they were physically present.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital content onto the real world, typically through devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses. Examples include Pokémon GO and Snapchat filters, where digital elements enhance the physical environment.
- Mixed Reality (MR): MR combines elements of both VR and AR, allowing real and virtual worlds to interact in real-time. Devices like Microsoft’s HoloLens enable users to manipulate digital objects that coexist with the physical environment.
Enhancing Remote Work with XR
Immersive Collaboration
One of the primary challenges of remote work is maintaining effective collaboration among team members. XR technologies can create immersive virtual environments where remote teams can meet, brainstorm, and collaborate as if they were in the same physical space. VR platforms like Spatial and AltspaceVR offer virtual meeting rooms where participants can interact with 3D objects, share presentations, and engage in discussions, creating a sense of presence and engagement that traditional video conferencing tools often lack.
Virtual Training and Onboarding
Training and onboarding new employees in a remote setting can be challenging. XR can provide interactive and engaging training experiences that simulate real-world scenarios. For instance, VR training modules can immerse new hires in virtual environments where they can practice tasks, receive feedback, and learn at their own pace. This approach not only enhances retention but also allows for safe, hands-on experience without the risks associated with real-world training.
Remote Assistance and Support
AR can be particularly useful for providing remote assistance and support. For example, a technician in a remote location can use AR glasses to receive real-time guidance from an expert who overlays instructions and annotations onto the technician’s field of view. This capability can significantly reduce downtime, improve troubleshooting efficiency, and enhance the overall support experience.
Overcoming Challenges
While XR technologies offer numerous benefits for remote work and collaboration, they also present certain challenges that need to be addressed:
Accessibility and Cost
High-quality XR equipment, such as VR headsets and AR glasses, can be expensive, making it difficult for some organizations to adopt these technologies on a large scale. Additionally, not all employees may have access to the necessary hardware or possess the technical skills to use XR effectively. To overcome this challenge, companies can explore cost-effective alternatives, such as mobile-based AR applications or web-based VR platforms, which require less specialized hardware.
Connectivity and Bandwidth
XR experiences often require high-speed internet and substantial bandwidth to function smoothly. In areas with limited connectivity, this can pose a significant barrier to adoption. In order to properly utilise XR technologies, organisations must make investments in a strong IT infrastructure and guarantee that remote workers have dependable internet connectivity.
Privacy and Security
The use of XR in remote work raises important privacy and security concerns. Applications for augmented reality and virtual worlds have the ability to gather sensitive data, including audio and visual data. Ensuring the security of this data and protecting user privacy is crucial. Companies must implement strict data protection policies, use secure platforms, and educate employees on best practices for maintaining privacy and security in XR environments.
Future Potential of XR in Remote Work
XR has enormous potential for distant work and collaboration, and it keeps growing. The following developments and trends are probably going to influence how XR is implemented in the workplace going forward:
Enhanced Realism and Interactivity
Even more interactive and realistic experiences will be possible with future XR technology. Advances in graphics, haptic feedback, and motion tracking will enable users to engage with virtual environments in ways that closely mimic real-world interactions. This heightened realism will further enhance the sense of presence and immersion in remote collaboration.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The integration of XR with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) will unlock new possibilities for remote work. AI-powered virtual assistants can facilitate meetings, transcribe conversations, and provide real-time insights, while ML algorithms can personalize training experiences based on individual learning styles and performance.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
To maximize the adoption of XR, cross-platform compatibility will be essential. Seamless integration between different XR devices and platforms will enable users to collaborate without being constrained by hardware limitations. This interoperability will foster a more inclusive and flexible remote work environment.
Expansion into New Industries
While XR is already making waves in industries like gaming and entertainment, its applications in remote work are expanding into various sectors, including healthcare, education, and manufacturing. For example, surgeons can perform remote consultations using AR, educators can create immersive virtual classrooms, and manufacturers can conduct remote inspections and maintenance using MR.
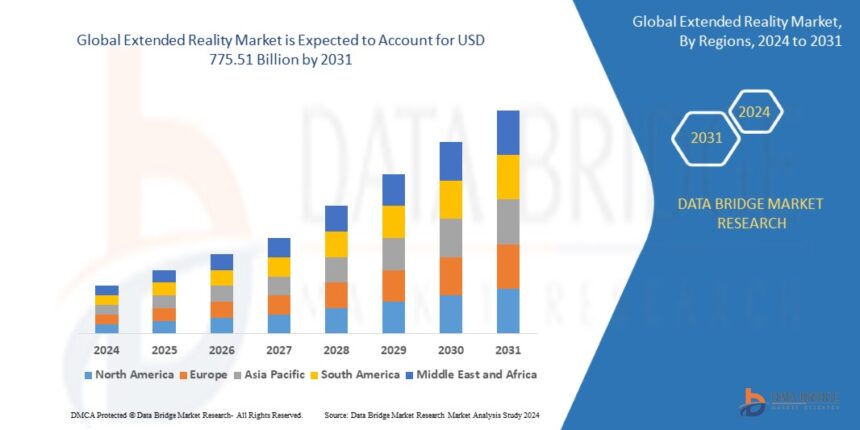
Growth Rate of Extended Reality Market
With a predicted value of USD 775.51 billion by 2031 and a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.57% from 2024 to 2031, the global extended reality market was estimated to be worth USD 91.80 billion in 2023.
Learn more: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-extended-reality-market
Conclusion
Extended Reality (XR) technologies have the potential to revolutionize remote work and collaboration by creating immersive, interactive, and engaging experiences. XR provides creative answers to the problems associated with working remotely, ranging from online training and meetings to remote help and support. However, to fully realize the benefits of XR, organizations must address challenges related to accessibility, connectivity, and security. As technology continues to advance, the future of XR in remote work looks promising, with enhanced realism, AI integration, cross-platform compatibility, and applications across diverse industries paving the way for a more connected and productive remote workforce. Embracing XR is not just a trend but a strategic move towards a more flexible, efficient, and collaborative work environment.